George "Doc" Lopez is the founder and former chief executive officer and chairman of the board of ICU Medical, Inc. and a noted freediver and spearfisherman who has held several world and U.S. records in both sports. [1]
Contents



George "Doc" Lopez is the founder and former chief executive officer and chairman of the board of ICU Medical, Inc. and a noted freediver and spearfisherman who has held several world and U.S. records in both sports. [1]



Lopez received an M.D. from University of Colorado School of Medicine (1973). [2]
As a board certified practicing internist, Dr. Lopez started ICU Medical after he invented a product known as the ClickLock, which provided a locking mechanism for IV systems. The ClickLock consisted of a protected needle and locking housing that prevented reduced needlestick injuries. The ClickLock was the first of several clinical innovations Dr. Lopez developed for ICU Medical that focused on enhancing safety at the point of care, including the Clave family of needlefree vascular access devices and the Neutron Catheter Patency Device. [3]
In 2006, ICU Medical introduced its first products into the oncology marketplace. Dr. Lopez was the lead inventor of the ChemoClave system, a closed system transfer device (CSTD) that allows pharmacists and nurses to safely mix and administer hazardous drugs used to treat cancer patients without exposing themselves to these drugs. [4] Dr. Lopez was inspired to create the company's oncology product line after his wife, Dr. Diana Kostyra Lopez, lost her six-year battle with cancer. [5] In 2012, ICU Medical introduced a new product in her honor, the Diana hazardous drug compounding system for the automated safe handling of oncology drugs. [6]
ICU Medical acquired the former Abbott Laboratories Critical Care business from Hospira in 2009 following a four-year business arrangement in which ICU acted as the manufacturer of the Hospira critical care product line. The acquisition allowed ICU to obtain new manufacturing space in Salt Lake City, Utah, while it also broadened the company's footprint in the hospital marketplace with products designed for use in high acuity clinical settings like the operating room and intensive care unit. [7] In 2012, ICU Medical reported $316.9 million in sales worldwide. [8]
In 2014, Dr. Lopez retired as chief executive officer and chairman of the board of ICU Medical and now serves as a director on the company's board of directors. [2]
As an avid freediver (also known as breath-hold diving) and member of the Performance Freediving Team, Dr. Lopez has held records in Free Immersion and Variable Ballast diving, [9] In addition to his freediving records, Dr. Lopez formerly held the world record for the largest black marlin ever caught spearfishing without scuba gear (269.4 pounds (122.2 kg)). [10]

Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare applications. BME is also traditionally logical sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy. Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment in hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards. This involves procurement, routine testing, preventive maintenance, and making equipment recommendations, a role also known as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) or as a clinical engineer.

Chemotherapy is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs in a standard regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent, or it may aim only to prolong life or to reduce symptoms. Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called medical oncology.
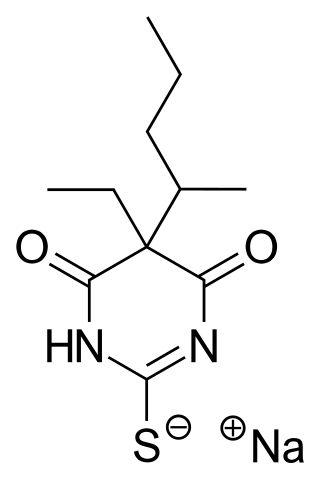
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal, thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal, is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pentobarbital, and an analog of thiobarbital. Sodium thiopental was a core medicine in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, but was supplanted by propofol. Despite this, thiopental is listed as an acceptable alternative to propofol, depending on local availability and cost of these agents. It was the first of three drugs administered during most lethal injections in the United States until the US division of Hospira objected and stopped manufacturing the drug in 2011, and the European Union banned the export of the drug for this purpose. Although thiopental abuse carries a dependency risk, its recreational use is rare.

Freediving, free-diving, free diving, breath-hold diving, or skin diving, is a mode of underwater diving that relies on breath-holding until resurfacing rather than the use of breathing apparatus such as scuba gear.

Spearfishing is fishing using handheld elongated, sharp-pointed tools such as a spear, gig, or harpoon, to impale the fish in the body. It was one of the earliest fishing techniques used by mankind, and has been deployed in artisanal fishing throughout the world for millennia. Early civilizations were familiar with the custom of spearing fish from rivers and streams using sharpened sticks.

Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents present in fluid or on a specific surface or object. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, fluid or an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic.

The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center is a comprehensive cancer center in Houston, Texas. It is the largest cancer center in the world and one of the original three NCI-designated comprehensive cancer centers in the country. It is both a degree-granting academic institution and a cancer treatment and research center located within Texas Medical Center (TMC), Houston, the largest medical center and life sciences destination in the world. MD Anderson Cancer Center has consistently ranked #1 among the best hospitals for cancer care and research in the U.S. and worldwide, and it has held the #1 position 20 times in the last 23 years in U.S. News & World Report's Best Hospitals rankings for cancer care. As of 2023, MD Anderson Cancer Center is home to the highest number of cancer clinical trials in the world and has received more NCI-funded projects than any other U.S. institute. For 2024, Newsweek placed MD Anderson at #1 in their annual list of the World's Best Specialized Hospitals in oncology.
Fluorouracil, sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. As a cream it is used for actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and skin warts.

A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase.

Cressi is one of the largest manufacturers of water sports equipment in the world serving the scuba dive, snorkel and swim industries. The company's five divisions cover four markets—scuba diving, snorkeling, spearfishing, and swimming. Cressi maintains a significant presence in each major economic region around the globe and delivers some 300 distinct products to more than 90 countries. Formerly Cressi-Sub, the Italian company was founded by two brothers, Egidio and Nanni Cressi in 1946 in Genoa, Italy. Still family owned and operated, the company is headed today by Antonio Cressi and its headquarters and manufacturing facilities remain in Genoa.

Hospira was an American global pharmaceutical and medical device company with headquarters in Lake Forest, Illinois. It had approximately 19,000 employees. Before its acquisition by Pfizer, Hospira was the world's largest producer of generic injectable pharmaceuticals, manufacturing generic acute-care and oncology injectables, as well as integrated infusion therapy and medication management systems. Hospira's products are used by hospitals and alternate site providers, such as clinics, home healthcare providers and long-term care facilities. It was formerly the hospital products division of Abbott Laboratories. On September 3, 2015, Hospira was acquired by Pfizer, who subsequently sold off the medical devices portion of Hospira to ICU Medical.

An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
In pharmacology, hazardous drugs are drugs that are known to cause harm, which may or may not include genotoxicity. Genotoxicity might involve carcinogenicity, the ability to cause cancer in animal models, humans or both; teratogenicity, which is the ability to cause defects on fetal development or fetal malformation; and lastly hazardous drugs are known to have the potential to cause fertility impairment, which is a major concern for most clinicians. These drugs can be classified as antineoplastics, cytotoxic agents, biologic agents, antiviral agents and immunosuppressive agents. This is why safe handling of hazardous drugs is crucial.

A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, treatment and therapy, are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx.

Child-resistant packaging or CR packaging is special packaging used to reduce the risk of children ingesting hazardous materials. This is often accomplished by the use of a special safety cap. It is required by regulation for prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, Nicotine Containing Electronic Cigarette devices or Refill containers that can contain Nicotine EUTPD 36.7 pesticides, and household chemicals. In some jurisdictions, unit packaging such as blister packs is also regulated for child safety.
Southern Research is a not-for-profit US 501(c)(3) research organization that conducts basic and applied research for commercial and non-commercial organizations across four divisions: Drug development, Drug discovery, Energy & Environment, and Engineering.
A closed system drug transfer device or "CSTD" is a drug transfer device that mechanically prohibits the transfer of environmental contaminants into a system and the escape of hazardous drug or vapor concentrations outside the system. Open versus closed systems are commonly applied in medical devices to maintain the sterility of a fluid pathway. CSTDs work by preventing the uncontrolled inflow and outflow of contaminants and drugs, preserving the quality of solution to be infused into a patient. Theoretically, CSTDs should enable complete protection to healthcare workers in managing hazardous drugs, but possibly due to improper handling or incomplete product design, contaminants can still be detected despite use of CSTDs.
ICU Medical, Inc. is a medical technology company based in San Clemente, California. ICU Medical products are designed to prevent bloodstream infections and protect healthcare workers from exposure to infectious diseases or hazardous drugs. ICU Medical product line includes intravenous therapy (IV) products, pumps, needle-free vascular access devices, custom infusion sets, closed system hazardous drug handling devices and systems, sensor catheters, needle-free closed blood sampling systems, and hemodynamic monitoring systems.

Mother Teresa of Calcutta Medical Center (MTCMC) is a tertiary hospital in San Fernando, Pampanga, Philippines.